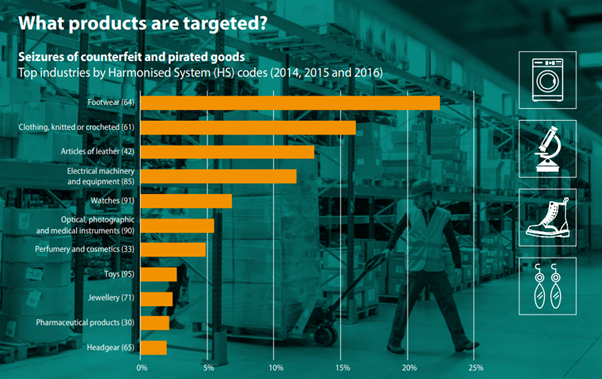
The counterfeiting merchandise market has boomed over the last few years. Counterfeit sales impact hundreds of industries at large every year, from high-margin gadgets and luxury goods to low-priced consumer goods.
In 2020, the total loss incurred by luxury brands due to counterfeit and pirated products amounted to USD 50 billion, only in the clothing and cosmetics industries.
According to a joint report (Global Trade in Fakes) by OECD and EUIPO, counterfeit merchandise trade amounted to a staggering USD 464 billion, accounting for 2.5% of global trade in 2019. To put that into context, it was higher than the GDP of Ireland in the same year, which stood at USD 399 billion.
And the issue is intensifying due to the surge in production in countries like China, which accounts for 89% of the seized fake goods. This knockoff boom feeds a big demand online, and the internet only makes it easier. Keeping traders anonymous and moving fake sales from street corners to a worldwide market costing legitimate businesses tons of revenue every year.
Counterfeiting: The Real Cost to Business
The International Chamber of Commerce reports that these illegal activities siphon off billions that could otherwise support legitimate businesses. They fuel a shadow economy, cutting into government revenues needed for essential public services and increasing the financial burden on taxpayers.
As per a Statista report, the annual sales losses from counterfeiting in various sectors are staggering. For instance, the clothing sector alone faced losses of 26.3 billion euros in 2020. The World Trademark Review highlights the global impact of counterfeiting and piracy, noting that transnational criminal organizations continue to exploit the low risk and high reward of counterfeiting crimes.
The FMCG sector is particularly vulnerable to counterfeiting. An article on ET Retail discusses the detrimental impacts of counterfeiting in the FMCG industry, emphasizing the erosion of brand reputation and consumer health and safety concerns. Counterfeit incense sticks, for example, not only affect economic dynamics but also tamper with cultural traditions. This means the impact extends beyond revenue loss.
Impact on brand image
When counterfeit items dominate the market, it can significantly damage the reputation of authentic brands. Buyers mistake these counterfeits for genuine products, leading to a decline in the perceived brand quality.
In every market, price is a major factor for a massive portion of the customer base. So, some customers may be fully aware and deliberately buy knockoffs.
The real issue arises when customers unknowingly purchase counterfeit items. These customers, unaware they have bought a fake, face product issues and naturally react negatively. Their dissatisfaction is vocalized within their networks, inadvertently damaging the brand’s reputation. It is a situation that highlights the indirect impact counterfeit goods can have on legitimate businesses, affecting their brand perception and customer trust.
According to Keith Goldstein of VerifyMe, as reported by Forbes, counterfeiting is responsible for 2.5 million lost jobs globally. IncoPro found that 52% of consumers lost trust in a brand after purchasing a fake good online.
Reduction in stock holds of retailers and distributors
If the demand for cheaper counterfeits rises, retailers and online distributors may reduce their stock of authentic products in response to it. This reduction in legitimate distribution channels further undermines the market presence of the original brands.
Moreover, although fake, low-cost counterfeits exert pressure on authentic brands to decrease their pricing, directly affecting their profit margins.
Legal liabilities on brands
In critical sectors such as pharmaceuticals, automotive, aviation, and electronics, counterfeit products pose severe safety risks. These risks translate into increased legal liabilities for authentic brands, as they are mistakenly held responsible for defects in counterfeit products.
Higher customer service costs
Authentic brands also incur higher customer service and warranty support costs when consumers, having unknowingly purchased counterfeit items, seek help.
Marketing expenses escalate as counterfeit sellers drive up the cost of paid search advertising and disrupt the effectiveness of authentic brands’ search engine optimization (SEO) efforts.
Impact on customer loyalty
Negative experiences with counterfeit products mistakenly believed to be genuine eat into the trust in the authentic brand. It is hugely detrimental to the brand’s relationship with its customers.
Blockchain Adoption to Deter Counterfeiters
Traditionally, industries have grappled with distinguishing authentic products from fakes. Holographic stickers or barcodes are no longer sufficient, as counterfeiters can now replicate these, too. Now, blockchain is stepping in as a powerful tool to change this narrative.
At its core, blockchain creates a transparent and unchangeable record of a product’s journey, from its creation to its final sale. This means every step in a product’s life can be tracked and verified, offering an unmatchable level of traceability.
Manufacturers can now tag each product with a unique digital identifier on the blockchain, ensuring its authenticity can be confirmed at any stage in the supply chain. This makes it harder for counterfeiters to infiltrate the market and builds consumer confidence in the authenticity of the products they purchase.
Key Features of Blockchain in Combating Counterfeits:
- Immutable Ledger: Blockchain creates an unchangeable record of a product’s history, from its origin through the entire supply chain. Each transaction or ownership change is securely recorded and time-stamped, ensuring transparent provenance tracking and authenticity verification.
- Unique Identifiers: By assigning a digital token or unique identifier to each genuine product and recording it on the blockchain, manufacturers and consumers can easily verify a product’s authenticity. This system makes it extremely difficult for counterfeiters to replicate genuine products.
- Instant Verification: Consumers can use smartphones and blockchain-powered apps to scan a product’s QR code or NFC tag, accessing its blockchain records for immediate verification.
While blockchain shows great promise in combating counterfeit goods, we must address scalability, interoperability, and regulatory concerns. As the technology matures, we expect these challenges to be overcome.
Leading Brands Using Blockchain to Counter Counterfeits
- Amazon teamed up with Nestle to develop a blockchain system that tracks the journey of chocolate beans. It provides detailed information about the planting, roasting, and growth conditions of the beans, ensuring transparency and authenticity.
- Alibaba, a giant in online retailing, requires fashion brands to upload their designs into its blockchain system. It helps prove the products’ originality and combat counterfeit goods effectively.
- Luxochain, a Swiss company, has developed a blockchain certification service for luxury goods. It allows luxury brands and consumers to verify the authenticity of products before purchase. It combines blockchain with NFC, RFID, fingerprint authentication, and Block ID technologies. Davide Baldi, CEO of Luxochain, emphasizes the role of blockchain in revolutionizing the luxury market, stating, “We want to build a better world, where counterfeit and stolen goods can be easily identified by a mobile phone.”
- NITI Aayog, in partnership with Oracle, Apollo Hospitals, and Strides Pharma Sciences, is piloting a real drug supply chain using blockchain and IoT software in India. This initiative aims to tackle the problem of fake drugs by enabling real-time monitoring and verification of drugs from manufacturing to consumer purchase.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Blockchain:
Implementing blockchain can be complex and costly. Businesses must evaluate some key factors like:
- Supply Chain Complexity: The more complex a supply chain, the more resources are needed for blockchain integration. This includes both technological infrastructure and training.
- Product Value: The decision to implement blockchain is often more viable for high-value products where the impact of counterfeiting is more significant.
- Industry-Specific Counterfeiting Rates: Industries heavily affected by counterfeiting are more likely to benefit from blockchain due to its ability to secure product authenticity.
- Customization Needs: Blockchain solutions must be tailored to specific business requirements, including integrating existing systems and processes.
For EU companies, particularly those dealing with international suppliers, a careful cost-benefit analysis is essential. They need to determine if the financial advantages of using blockchain to protect against counterfeiting outweigh the implementation and operational costs. It’s a crucial decision, especially in a global business environment where supply chains and counterfeiting risks vary greatly.
Industries Adopting Blockchain for IP Verification:
- Luxury Goods: Luxury fashion brands use blockchain to verify the authenticity of their products, allowing customers to confirm the legitimacy of their purchases through QR codes.
- Pharmaceuticals: It helps combat counterfeit drugs by enabling real-time tracking from the manufacturer to the consumer, thus maintaining the integrity of the supply chain.
- Food Safety: It is employed in the food industry to monitor and trace the origin of products. This helps prevent counterfeit food products and enhances food safety by quickly identifying contamination sources during recalls.
Conclusion
Addressing counterfeiting is crucial for any business, given its far-reaching impact on revenue, customer relationships, brand reputation, and legal standing. Ignoring this issue is not an option.
But the good news is that blockchain is bringing forth the right approach to beating counterfeits. It streamlines the process, making it efficient and manageable without significantly overhauling your organization or expanding your team.
The focus of brands should extend beyond distribution channels and encompass the promotional tactics used to sell counterfeit goods. The fight against counterfeiting requires a concerted effort from brands, consumers, and authorities to protect the integrity of genuine products and the safety of consumers.
About the author
Dan Weinberger, UN Supply Chain Expert and CEO of Morpheus.Network